This publication is intended as a learning resource, all answers are documented and explained. Datasets are available in R packages. 1. The R language is a dialect of which of the following programming languages?When the page is scrolled to the very beginning, so that the top/left corner of the window is exactly the document top/left corner, these coordinates The method elem.getBoundingClientRect() returns window coordinates for a minimal rectangle that encloses elem as an object of built-in DOMRect class.They also show that when the net external force acting on the system is zero, the velocity of the center of mass will be constant. A ball of mass m and radius R is placed inside a spherical shell of the same mass m and inner radius 2R (see Figure 9.6a). The ball is released and moves back and forth before...These coordinates are calculated relative to the station frame (coordinate system associated with the technological station) or relative to the base frame The calculated location coordinates make it possible for the robot to automatically approach the object and carry out the technological operations.Asked 6 years, 10 months ago. for calculating my 3D coordinates but I have no constant as the link explains for calculating s.My target rotates about the x axis in the This is equivalent to positioning an object coordinate system on the plane in such a way that Z=0. 2. Note that this effectively kills a third...
Coordinates
see how come displacement is 10 0 10 -20 can u explain. Draw a labelled ray diagram for the formation of image by a convex lens of focal length sum when the object is place at a distance of 25cm form the le … ns.Use spherical coordinates for the first and cylindrical coordinates for the second. 10.7K views ·. However, if you're asking coordinate-invariant questions that can be expressed purely in terms of the quantities themselves rather than the individual coordinates, then the answer will also be the same.In Coordinate Geometry of Class 9, we learned what is x and y coordinate of a point. In this chapter, we will learn. Coordinates of points in x-axis Using properties of parallelogram to do some questions on Section Formula (like finding coordinates of a point, when 4 vertices of parallelogram are given).The definition of free software consists of four freedoms (freedoms 0 through 3). Which of the following is NOT one of the freedoms that are part of the definition? The freedom to prevent users from using the software for undesirable purposes.

9. systems of particles
Thus, the acceleration of the object in the first configuration is at an angle of from horizontal. Part (b): In the second configuration as shown in the figure Two forces, 5.0 kg object, acceleration of the object,F1=20 N, F2=15 N, for the configurations, net force, horizontal direction, vertical direction...The object is pulled 0.60 m to the right and released at time t = 0 s. What will be the object's x-coordinate when t = 0.64 s? x = A cos (ωt) To find x What is the maximum velocity of an object in a spring-mass system in which the angular frequency is 10 rad/s, and the amplitude is 0.40 m?An opaque object with a height of h moves toward the wall with constant velocity v of magnitude v. At time t=0 , the object is located at the source S. (A) What is the x-coordinate of the object when t = 10.0 s?Local coordinates are the coordinates of your object relative to its local origin; they're the coordinates your object begins in. When creating an orthographic projection matrix we specify the width, height and length of the visible frustum.Coordinates in an inertial reference frame give physical times and distances as measured by an observer at rest in that frame. The coordinates of dierent inertial observers are related by Lorentz transformations. For example, a Lorentz boost in the x-direction relates coordinates in the two...
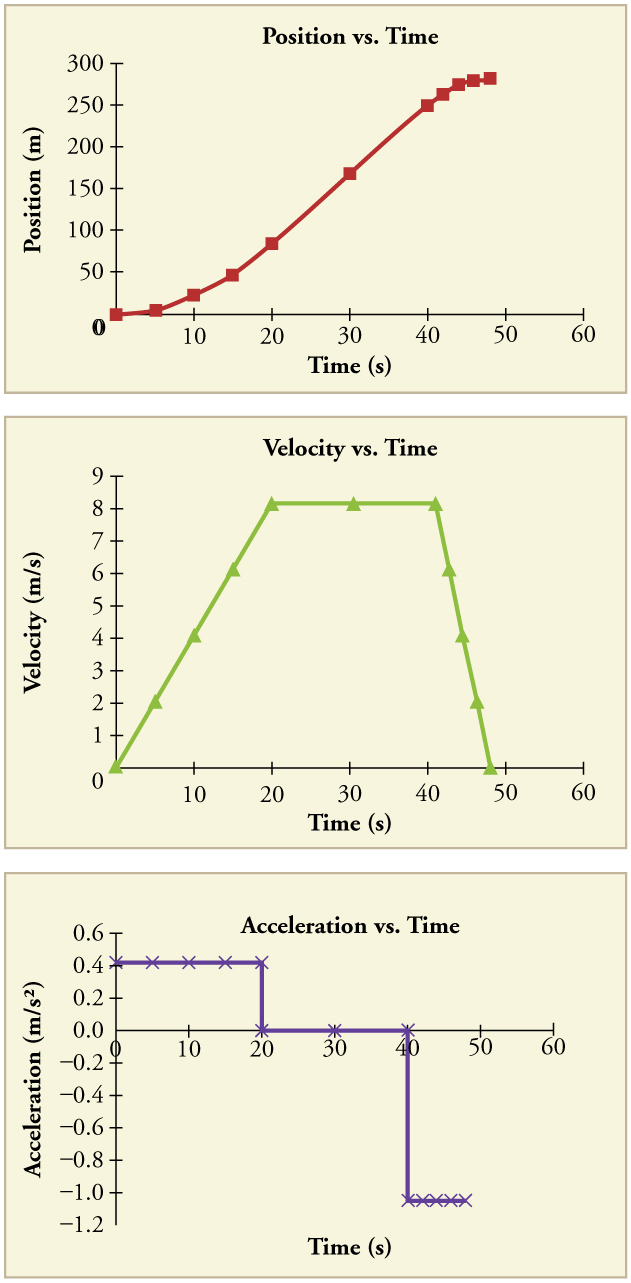
I imagine your query is in response to the equation for acceleration of
a(t) = -0.0320(15.0 - t)
You cannot use equations for consistent acceleration (kinematic equations) because acceleration varies with time.
One should integrate the accelerations to find velocity.
One must combine the velocities to find place.
a(t) = -0.0320(15.0 - t)
a(t) = 0.032t - 0.480
v(t) = ∫ a(t)dt
v(t) = ∫ 0.032t - 0.480 dt
v(t) = 0.016t² - 0.48t + C
we're instructed that v(0) = 6.90
6.90 = -0.48(0) + 0.016(0)² + C
C = 6.90
so the equation for velocity is
v(t) = 0.016t² - 0.48t + 6.90
To to find place, we combine again
s(t) = ∫ v(t)dt
s(t) = ∫ 0.016t² - 0.48t + 6.90 dt
s(t) = ⅓0.016t³ - 0.24t² + 6.90t + C
s(0) = -14.0
-14.0 = ⅓0.016(0)³ - 0.24(0)² + 6.90(0) + C
C = -14.0
so the equation for place is
s(t) = ⅓0.016t³ - 0.24t² + 6.90t - 14.0
now plug in the time in query t = 10.0
s(10.0) = ⅓0.016(10.0)³ - 0.24(10.0)² + 6.90(10.0) - 14.0
s(10.0) = 36.33333333
s(10.0) = 36.Three m
To the 3 important figures of the query.
I am hoping this helped.
Please take into account to vote a "Best Answer" from among your results. It's excellent karma as it keeps issues in balanced trade.
Introduction To Physics
2.8 Graphical Analysis Of One-Dimensional Motion – College Physics: OpenStax

Practice Problems
Physics Answers

PracticeTest1Solutions

An Object Moves In Along The X-axis With An Acceleration Given By: A = 4t (m/s2).... - HomeworkLib

Practice Problems
Solution Manual For Physics For Scientists And Engineers Foundations And Connections 1st Edition By By Nbzmr87 - Issuu

Mastering Physics Solutions Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics - A Plus Topper

Introduction To Physics
Physics For Scientists & Engineers With Modern Physics - Dobglas C. Giancoli

Falling Objects | Physics

7.5: Acceleration - Chemistry LibreTexts

Untitled
Solutions Manual For University Physics With Modern Physics 2nd Edition By Bauer By Phillips111 - Issuu

Tr313: FLAIR User Guide

Acceleration | Physics
0 comments:
Post a Comment